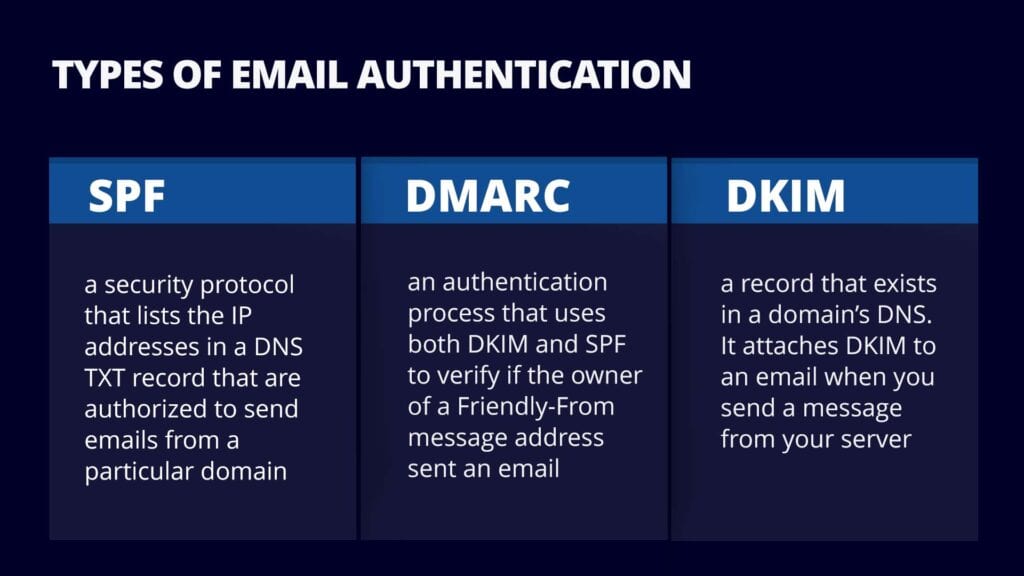
Every business needs to implement SPF DKIM and DMARC as essential measures for protecting email integrity.
Email functions as the essential communication tool for digital business operations. Numerous small and medium businesses fail to address the security threats which exist in their email systems. The early 2000s brought forth Sender Policy Framework or SPF as a solution to fight email spoofing. Attackers use this method to fake sender addresses so their fake emails seem authentic. Domain owners utilize SPF to define which servers are authorized to deliver emails from their domain. Receiving mail servers perform checks against authorized sender lists when SPF is configured correctly to verify message authenticity. The absence of SPF makes it possible for attackers to mimic company domains thus causing damage to reputation and triggering phishing attacks and dangerous security threats. Small and mid-sized businesses remain highly exposed because they lack internal security teams that monitor these stealthy email trust violations.
DKIM
The authentication protocol DKIM identifies email tampering during message delivery through its verification process. The IETF standardized DKIM after Yahoo and Cisco engineers developed it as a cryptographic signature system that embeds verification codes into email headers. The signature creation process utilizes private keys before recipients verify messages through DNS-published public keys. The email authentication process proves that the email contents stayed unmodified while confirming its domain of origin. For small businesses, this matters immensely. The time has passed when sending emails alone could ensure delivery success. Modern mailboxes operated by Google and Microsoft along with others base their inbox spam decisions on DKIM validation checks. Organizations that do not implement DKIM risk having their proposals and client communication and workflows disrupted while the sender remains unaware of the issue.
DMARC
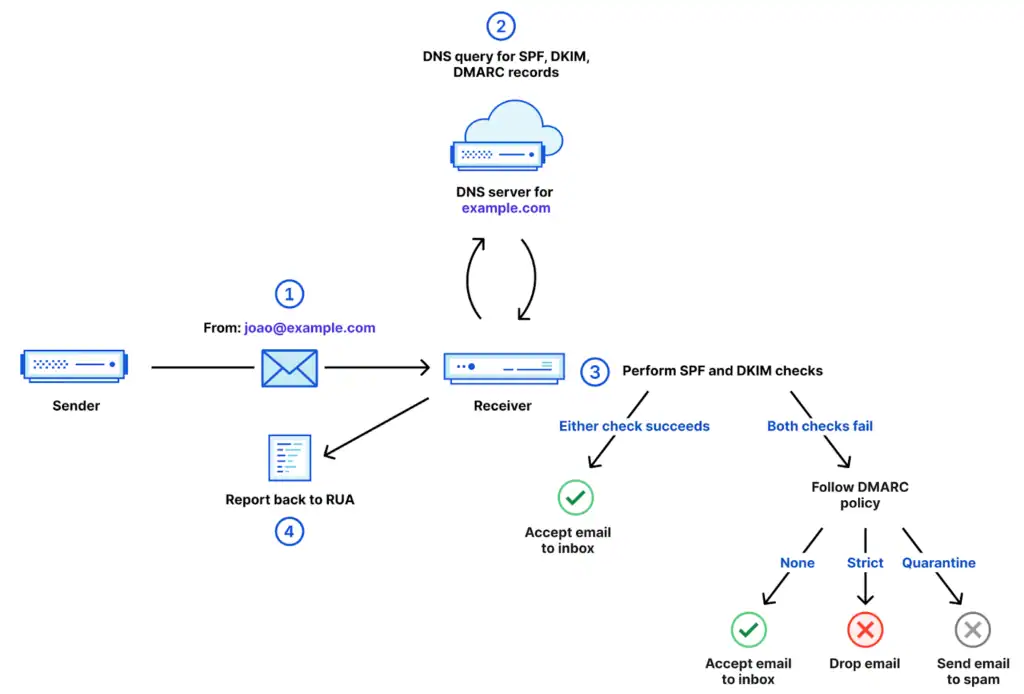
The email protection mechanism DMARC stands as the least understood yet most powerful email protection system even though it is also known as Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance. The authentication features of SPF and DKIM receive support from DMARC through its enforcement capabilities. The industry created DMARC in 2012 as an answer to increasing email fraud threats to enable domain owners in specifying receiving mail provider actions when SPF or DKIM authentication fails. Domain owners gain the ability to track email senders on their behalf through DMARC reporting while receiving information about message validation results. The protective shield of DMARC works alongside its dashboard functionality to protect businesses that require customer trust. The lack of DMARC protection allows fraudulent emails to bypass SPF or DKIM security checks and harm customer relationships. Your domain benefits from DMARC through rule control and report generation which allows you to increase enforcement capabilities as your domain grows.
Email Policies are imperative.
The implementation of email policies by dedicated IT and compliance teams primarily occurs within large enterprises while small and medium businesses rarely establish such protocols. The severe consequences of non-action remain the same regardless of the situation. Cybercriminals do not discriminate based on business size. Attackers select smaller organizations as their targets because these targets possess less complex systems to breach. Security firms and managed IT providers can set up SPF, DKIM and DMARC protocols for businesses with no disruption to operations. Your business email domain functions as your digital identification therefore it requires proper protection. Your office remains exposed to threats when the front door remains unlocked and your nameplate remains visible from outside. These controls have evolved from optional enhancements to essential requirements for industries such as healthcare and finance and legal services.
Do the neccessary
Organizations facing email deliverability problems and spam flags and customer phishing reports should implement these three protocols because they serve as critical solutions to rebuild and sustain customer trust. The authentication process through email plays an important role in maintaining successful marketing delivery rates. Your operational continuity depends on consistent delivery of newsletters together with proposals and invoice reminders and updates to customer inboxes. Unauthenticated domains will face negative consequences because Google and Microsoft continue to enhance their filtering algorithms. Businesses that take the necessary steps to implement SPF, DKIM and DMARC protect their operations from impersonation attempts and fraud while building resilient communication systems for the future digital environment that requires trust and accountability.



