Navigating SEC Cybersecurity Disclosure Rules: A Comprehensive Guide
In December 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) introduced new regulations aimed at enhancing cybersecurity risk management, governance, and incident disclosure among public companies. These rules are designed to improve transparency and protect investors by ensuring that organizations adequately disclose significant cybersecurity risks and incidents.
As the first anniversary of these regulations approaches, many organizations continue to grapple with compliance challenges. This guide delves into the core requirements, practical steps for compliance, and the challenges organizations may face in aligning with the SEC’s cybersecurity disclosure rules.

Material Incident Reporting: Requirements and Best Practices
Overview
The SEC mandates that public companies disclose material cybersecurity incidents promptly. Specifically, organizations are required to file a Form 8-K within four business days of determining that a cybersecurity incident is material. This requirement underscores the importance of timely and transparent communication with investors and stakeholders.
Key Considerations
- Defining Materiality: Determining what constitutes a material incident can be complex. Generally, an incident is considered material if it significantly impacts the company’s operations, finances, or reputation. The SEC provides guidance on assessing materiality, emphasizing the need to consider both quantitative and qualitative factors.
- Content of Disclosure: The disclosure should include details about the nature, scope, and timing of the incident, as well as its potential impact on the company’s financial condition and operations. It is crucial to provide sufficient information to inform investors without compromising the company’s security posture.
Steps to Enhance Incident Reporting
- Establish Clear Criteria for Materiality: Develop internal guidelines to assess the materiality of cybersecurity incidents. This involves evaluating the potential financial, operational, and reputational impacts of an incident.
- Implement a Robust Incident Response Plan: Ensure that your organization has a well-defined incident response plan that includes procedures for assessing and reporting incidents. Regularly test and update this plan to address emerging threats.
- Train Key Personnel: Educate employees, especially those in legal, compliance, and IT departments, about the SEC’s reporting requirements and the company’s internal protocols for incident disclosure.
- Engage Legal Counsel: Consult with legal experts to navigate the complexities of disclosure requirements and to ensure that communications are compliant with SEC regulations.
Annual Cybersecurity Disclosures:
Governance and Oversight
Overview
Beyond incident-specific reporting, the SEC requires companies to provide annual disclosures detailing their cybersecurity risk management strategies and governance practices. These disclosures are typically included in Form 10-K filings and are intended to give investors insight into how companies are managing cybersecurity risks at a strategic level.
Governance Structures
- Board Oversight: Companies must describe the board’s role in overseeing cybersecurity risks. This includes detailing any committees responsible for cybersecurity and how the board is informed about cyber risks and incidents. Resources from organizations such as the National Association of Corporate Directors can offer valuable insights into effective board oversight.
- Management’s Role: Organizations should outline the responsibilities of senior management in managing cybersecurity risks. This includes the roles of the Chief Information Security Officer and other key executives. Guidance from groups such as the Information Systems Audit and Control Association can help define these responsibilities.
Risk Management Framework
- Policies and Procedures: Companies are expected to disclose their policies and procedures for identifying and managing cybersecurity risks. This includes risk assessment processes, mitigation strategies, and incident response plans. Leveraging frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework can provide a comprehensive approach.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Given the increasing reliance on third-party vendors, companies should address how they manage risks associated with third-party service providers. Best practices for managing third-party risks are widely available from resources such as the Center for Internet Security.
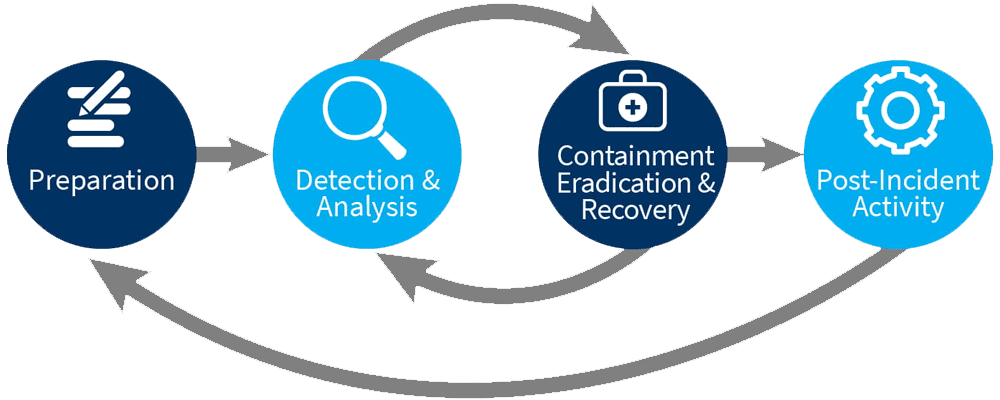
Developing and Maintaining a Robust Incident Response Plan
Importance of a Strong Incident Response Plan
An effective incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of cybersecurity incidents. It enables organizations to detect, respond to, and recover from incidents efficiently, reducing potential damage and facilitating compliance with reporting requirements.
Components of a Comprehensive Plan
- Preparation: Establish and train an incident response team, define roles and responsibilities, and develop communication strategies.
- Detection and Analysis: Implement monitoring tools to detect anomalies and potential incidents. Develop procedures for analyzing and confirming incidents.
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery: Develop strategies to contain the incident, eliminate the threat, and restore systems to normal operations.
- Post-Incident Activity: Conduct a post-mortem analysis to identify lessons learned and improve future response efforts.
Proactive Cybersecurity Risk Management Strategies
Why Risk Management Matters
Proactive risk management is essential for identifying and mitigating potential cybersecurity threats before they materialize into incidents. It involves continuous assessment and improvement of security measures to protect organizational assets.
Key Strategies
Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct periodic assessments to identify vulnerabilities and evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls.
Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices and their role in safeguarding information.
Endpoint Security Measures: Implement robust endpoint protection, including antivirus software, firewalls, and zero-trust architecture.
Addressing Challenges in Compliance
Common Challenges
Resource Constraints: Small to medium-sized enterprises often lack the dedicated resources to implement comprehensive cybersecurity programs.
Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it difficult to keep policies and defenses up-to-date.
Subjective Definitions: The determination of materiality can vary widely between organizations, leading to inconsistent reporting practices.
Solutions
Leverage Third-Party Expertise: Managed service providers can fill gaps in expertise and provide scalable solutions for cybersecurity and compliance.
Invest in Automation: Tools that automate monitoring, incident analysis, and reporting can reduce the burden on internal teams.
Stay Informed: Regularly review updates from regulatory bodies, including the SEC and CISA.
Wrap-up: Strengthening Cybersecurity and Compliance
The SEC’s cybersecurity rules emphasize the critical role of governance, transparency, and proactive risk management in today’s corporate landscape. Compliance is not just a regulatory obligation but a strategic opportunity to strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity posture and build trust with stakeholders.
Triton Technologies is committed to helping organizations navigate these challenges with tailored solutions for compliance and cybersecurity. Contact us at 866-304-4300 or visit our website at tritoncomputercorp.com for more information.



